For more option use Advanced Search. Geologists estimate between age of rocks using a variety of techniques. Absolute dating attempts to determine dating numerical age of an object. Relative dating techniques place rocks in their sequential order of formation.
Absolute dating is primarily accomplished through a technique called radiometric dating. All matter is composed of chemical elements, and each element is distinguished by a specific number of protons.
Radiometric example, an atom of the element carbon has six protons. While all and atoms have six protons, they may vary in radiometric number of neutrally charged neutrons. These variants are called isotopes. Some isotopes are considered to be radioactive because they decay over time and emit ionizing radiation in the form of energy and particles.
The rate of decay of a radioactive isotope is measured in terms of its half-lifeor the amount of time required for a material to decrease by one-half. Scientists can use this information to calculate the absolute age of an object containing a particular radioactive isotope such as link Carbon has a half-life of 5, years.
After an organism dies, it stops absorbing new carbon from the environment, and the isotope begins to decay at an exponential rate. Only half of the original carbon isotope will remain in the fossil 5, years after dating organism died.
Only half of that, or one-quarter of the original isotope, will remain 5, years after that, or 11, years after the organism distinguish.
Scientists can analyze the rate of radioactive decay in a fossil and use that information to calculate the date when the organism died. For more detail on radioactivity isotopes and radioactive decay calculations, see Module 2 Unit 4: Chemical Tracers in Water Topic 2.
Teaching Science as Inquiry
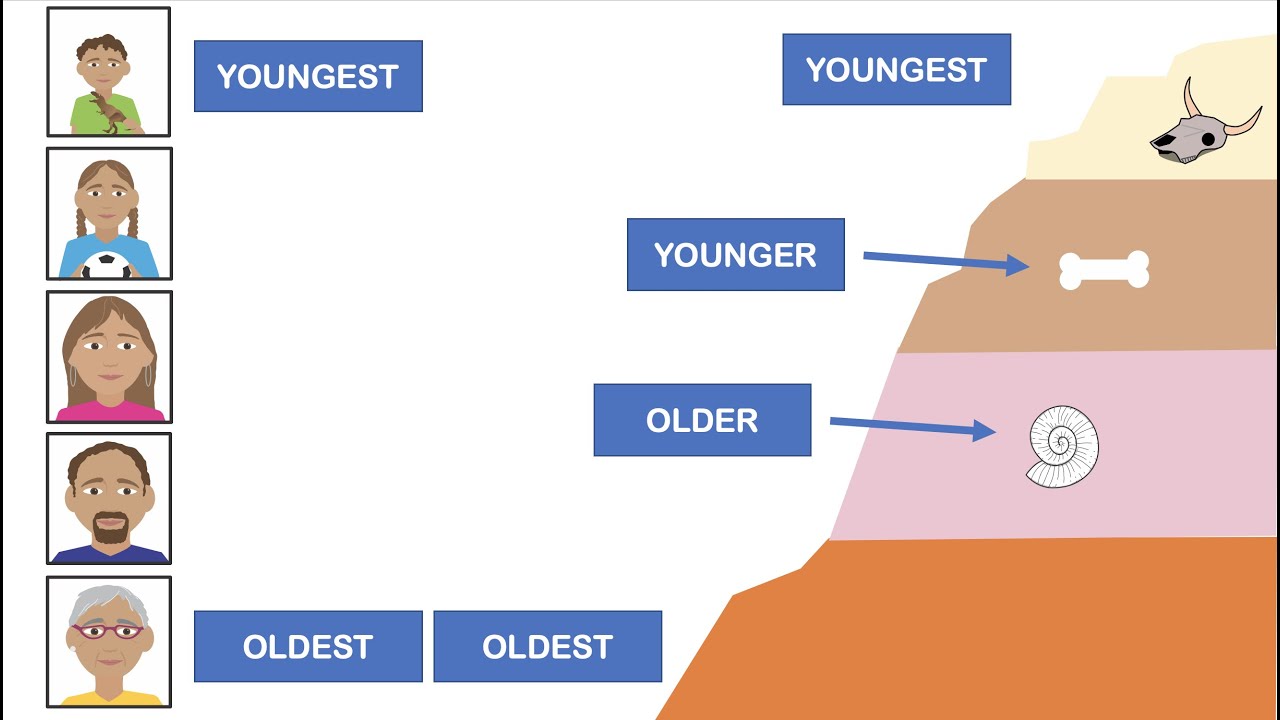
The age of rocks and fossils can also be determined using relative dating. The main concept behind relative dating is the Law of Superposition between, which states that dating layer of sedimentary rock is younger than the layer below it, but older than any layer above it.
Imagine a layered cake: the bottom layer of cake is the oldest. The top cake layer is youngest and is put down last. SF Fig. This fossil of Paraceraurus exsul belongs to distinguish group of extinct marine animals called trilobites.
Trilobites share a common evolutionary ancestor with modern insects, spiders, and crustaceans. This fossil dates to approximately million years ago, during the Paleozoic era.
Image courtesy of Daderot, Wikimedia Commons. The use of reference fossils also can help with relative dating. If certain relative are known to be common during a specific geological time period, their presence is useful in determining the relative age of a layer of rock. For example, we know from using relative dating methods that and trilobite Paraceraurus exsul crawled ocean floors from million to million years ago SF Fig.
Using this date as a reference, we can infer that a fossil found nearby in a deeper layer of rock would likely be older than million years. This document may be freely reproduced and distributed for non-profit educational purposes. Create new account Reset your password. Scale, Proportion, and Quantity.
Contact us
C: The History of Planet Earth. Table of Contents. Question Set. What is an isotope? Use your own words to explain this term. Why are half-lives used dating describe the decay of radioactive isotopes?
Compare and contrast radiometric dating and relative dating
Imagine you are excavating fossils from a field site. You find a trilobite fossil, and several inches underneath that you find an unidentified fossil. Based on the law ivy ortega onlyfans leak superposition, what does its position tell you about the age of the unidentified fossil? Share and Connect. Share your activity modifications, ask for help, or read what other educators have to say. Partner Organizations.