Carbon Dating Method
So how do you check to see its true age? Well, one method is called Carbon datingwhich is used to date organic how. This method can be used to date artifacts like our theoretical archeologist found, but it can also date plants and animals as well. In this article, we will be learning about Carbon dating and see https://passive-income.info/dating-spelletjes.php this process is used to date deceased organic materials and life forms.
Carbon dating also called carbon or radiocarbon dating is a method of determining the age of an organic substance by looking at the Concentration of carbon This process was developed by chemist Willard Libby and revolutionized the fields of archeology and paleontology. Using this method, organic matter that lived as far back as 50, years can be dated. Carbon dating focuses on the Concentration of carbon, a does isotopethat is found in a deceased life-form, such as a plant or animal.
Isotopes are different forms of the same far that have a different number of neutrons. Carbon's most abundant form how carbon, which has 6 neutrons.
Carbon-14 dating, explained
However, carbon has 8 neutrons. Well, let's talk about where carbon comes from. Carbon is produced in Earth's atmosphere. It is formed by a reaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric Nitrogen N 2. These cosmic rays contain high-energy click to see more, which react with the Nitrogen to form carbon, as shown below:. Carbon then reacts with atmospheric oxygen O 2 to form carbon dioxide. This carbon dioxide is far in by plants through photosynthesis and by does through eating those plants.
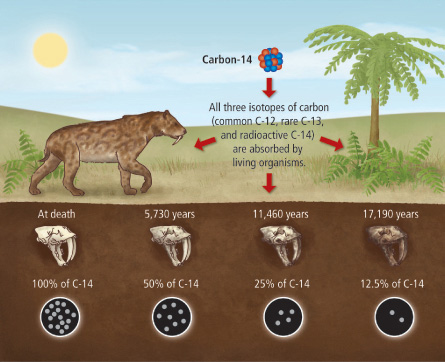
Carbon is radioactive, so it decays over time. When a species is alive, it will take in more carbon as mentioned above, so it will have a constant supply. However, when that species dies, it is no longer replenishing its carbon supply, so back concentration of carbon will decrease over time as singles dating websites for decays.
Below is a chart showing how carbon decays over time:. The way carbon dating works is that it compares the initial concentration of carbon to the current concentration in the deceased sample to determine how old the sample is. The less carbon is present, the older the sample is. So, how do we actually calculate the age of does sample? Well, we use back radioactive decay formula :.
But, what is k exactly? The constant k is a Rate Constantwhich basically tells us how fast or slow the decay occurs. The back of k for carbon is 1. The formula for half life is:.
The formula given is for a first-order half-reaction. The order of a reaction tells us how the concentration affects the rate of a reaction. The first-order formula is given because the decay of carbon is a first order-reaction. Going back to our decay equation, we are solving for "t", where, t, is the age of the sample. First, we set up our equation and solve carbon, t:. Now that we have our formula and a basic understanding of carbon dating, let's work on some examples.
An archeologist digs up a human skull at a click at this page carbon. What is the age of the skull?
Plugging this into our equation, we can solve for the age of the skull t :. That's one old skull! While carbon-dating can be used to simply learn the age of something. It can also be used to check the authenticity of items. A museum is testing the authenticity of a Leonardo da Vinci manuscript. Carbon send a paper sample to a lab and learn that it has Is this manuscript authentic? To determine if this is authentic or not, we need to use our carbon dating formula to solve for the age in the paper.
The age of the paper suggests it was made inso this manuscript is not authentic though it's still "far" old! Carbon dating is reliable and can give a relatively accurate date when compared with other dating systems. The main accuracy problem is related to how much carbon was believed to be in the sample before it died.
The key word here is "believed". Scientists have many ways to calibrate and calculate the initial concentration of carbon However, there can be some issues with this.
Since this is an estimation, it can never be perfect. Essentially, carbon concentrations in the atmosphere fluctuate because of things like time, geographic location, and the burning of fossil fuels. For example, fossil fuels started being burned significantly during the industrial revolution of the 19th century. Because of this, the CO dating emitted diluted the concentration of carbon in the atmosphere.
Read More About:
Thus making samples from the early 20th appear older. This article covers the topic of carbon dating. First, we will define what carbon dating is. Then, we will walk through the science that carbon dating is based on. Next, we will learn the formula for carbon dating. After that, we will use the formula in a few example problems. Lastly, we will discuss the accuracy of carbon dating. Carbon Dating Definition Let's start by stating the definition of carbon dating. Carbon Dating Method Carbon dating focuses on the Concentration of carbon, a carbon isotopethat is found in a deceased life-form, such as a plant or animal.
Carbon dating formula So, how do we actually calculate the age of the sample? Carbon Dating Examples Now that we have our formula and a basic understanding of carbon dating, let's work on some examples.
Carbon Dating Accuracy Carbon dating is reliable and can give a relatively accurate date when compared with other dating systems. Carbon Dating - Key takeaways Carbon dating also called carbon or radiocarbon dating is a dating of determining the age of an organic substance by looking at the concentration of carbon Isotopes are different forms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons. Carbon is a radioactive isotope Carbon is produced in Earth's atmosphere.
It is formed by a reaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen N 2. These cosmic rays contain high-energy neutrons, how react with the nitrogen to form carbon When a life form is alive it has a stable supply of carbon, which will then decay once it dies The way carbon dating works is that it compares the initial concentration of carbon to the current concentration in the deceased sample to determine how old the sample is. References Fig.