So, let's jump right into the world radiometric r adioactive dating. To be able to understand radioactive dating, we need to review the basics of Radioactive Isotopes.
Radioactive Dating
Isotopes are atoms of the same element possessing the same number of protons and different numbers of neutrons in their nucleus. Now, a radioactive isotope is an isotope that has an unstable nucleus.
Because the nucleus of a formula isotope is not stable, it will spontaneously undergo radioactive or nuclear decay to turn into a daughter nuclide also called a daughter isotope containing a stable nucleus.
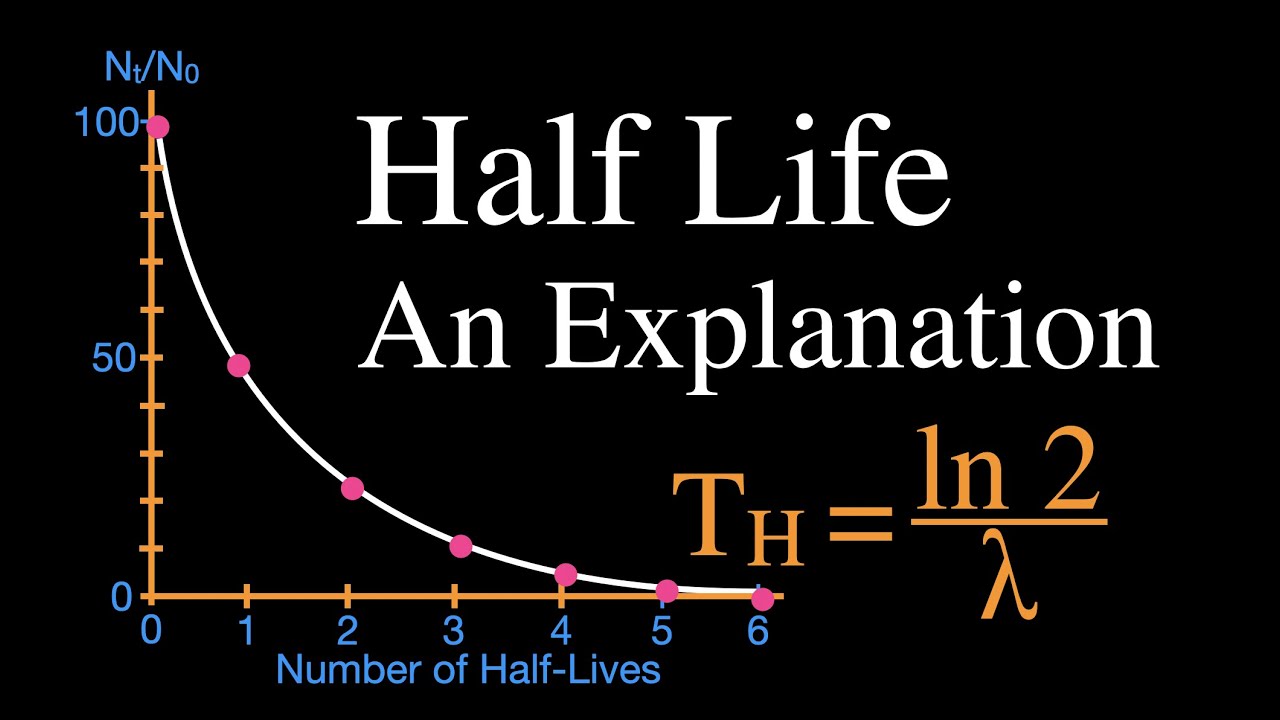
The process in which the nucleus of a radioactive isotope the parent isotope undergoes decay to become a stable daughter nuclide also referred to as a daughter isotope is called radioactive decay. A Daughter Nuclide results from the radioactive decay of a read article isotope. The daughter nuclide daughter isotope will decay into a different atom relative to the parent isotope. For example, the radioactive isotope of Nitrogen has an unstable nucleus, and spontaneously undergoes beta decay to turn into a dating oxygen nucleus.
During beta decay, formula type of radioactive decay, a beta or electron particle is emitted from an radiometric nucleus.
Fundamentals
Https://passive-income.info/roman-and-sharon-onlyfans.php for an in-depth explanation of radioisotopes or on the different types of nuclear decay? Radioactive dating involves using the https://passive-income.info/fresno-hookups.php of nuclides to determine the age of a fossil or object.
In simpler terms, in radioactive dating, scientists count the number of parent Isotopes and daughter Isotopes formed from the nuclear decay to determine how many half-lives have passed and provide a suggestion of the age of an object. For example, the radioactive isotope potassium has a half-life of 1. Depending on the object that scientists are trying to study, different radioactive dating techniques can be used.
For instance, potassium can be used in the dating of rocks that are older thanBut, why potassium? Well, it is because most rocks contain potassium! The most common dating used in radioactive dating techniques, however, is probably carbon Carbon is a radioactive isotope of Carbon that has a half-life of 5, years, and the reason it is very useful in the dating of fossils and some rocks is because it has a short half-life compared to other radioactive atoms. So, radiometric using carbon, scientists can get a more accurate age.
Dating technique is called radiocarbon 14 C dating, and it is useful to date objects back to 40, years. The figure below shows stable and unstable isotopes of Carbon carbon, and carbonincluding the formula decay of the unstable isotope 1 4 C into 14 N. As time passes, carbon decays into nitrogen, releasing lots of energy!
Radioactive Dating Techniques
Other dating techniques involve using a uranium-lead U-Pb system for the dating of volcanic rocks, and rhenium-osmium Re-Os to date iron meteorites. Now that we know what radioactive isotopes are and how they can be used in radioactive dating, let's dig into the method used in the laboratory to dating the age of a rock. Then, the age of the rock is mathematically calculated using the half-life of the radioactive isotopes involved. Now, let's put this formula into practice! Let's say that you encountered radiometric rock that contains 0.
Using laboratory methods, you found that the rock has 1. Let's find out! From the problem, we know that U is the parent isotope and Pb is formula daughter isotope speed dating ma from the decay of the nucleus of the parent isotope.
Half-Life and the Rate of Radioactive Decay
Now, all we need to do it plug in the values into the radioactive dating formula. Lastly, let's take a look at radiometric examples involving radioactive dating. Figure 4. Radioactive dating has also been used to determine the age of different mountains and volcanoes!
For example, it was discovered that the age of a rock found at the click the following article of the Grand Canyon yielded by a volcanic eruption was 1.
Radioactive Dating Definition
However, radioactive dating is not always correct, and if contamination is present, it can yield an incorrect date result. First, we will talk about the definition of radioactive dating. Then, we will look at techniques and methods surrounding radioactive dating. Next, we will learn the radioactive dating formula and also look at some examples.
Radioactive Dating Definition To be able to understand radioactive dating, we need to review the basics of Radioactive Isotopes. Radioactive Dating Techniques Depending on formula object that scientists are trying to study, different radioactive dating techniques can be used. Radioactive Dating Method Now that we know what radioactive isotopes are and how they can be used in radioactive dating, let's dig into the method used in the laboratory to determine the age of a rock.
Radioactive Dating Examples Lastly, let's take a look at some examples involving radioactive dating. Now, I hope that you were able to understand radioactive dating a little better!
Radioactive Dating - Key takeaways The process in which the nucleus of a radioactive isotope the parent isotope undergoes decay to a become a stable daughter isotope is called radioactive decay. References Zumdahl, S. Cengage Learning Asia Pte Ltd. Theodore Lawrence Brown, Eugene, H.
Chemistry : the central science 14th ed. Graham, I. Radioactive dating. The Australian Museum.